Captive portals almost always work by validating the IP address of the
client, and often the MAC address. This creates a wrong feeling of
security, because it is quite easy to bypass. Let’s explain the most
common problem: spoofing.
Installing a captive portal
I have chosen to install Alcasar, which
claims to be a highly secure solution developed by the French Ministry
of Defense.
First surprise, it’s a shell script ! In fact, it’s not really an
application, only an installer for a few packages, with some
configuration. Installation went pretty bad:
- the installer only works for a specific version of
Mandriva (2007), which is quite old,
and buggy on my hardware
- most things are hardcoded: the installer exploded without errors
because my network is not ending by a 0 (10.0.0.129/25)
- my third network card is not even used by the script ! Too bad for
the DMZ
After 4 or 5 retries, and modifications in the script, I finally got a
working server.
First tests
After a reboot, everything seems to work. Got an address using DHCP, I
try to connect to Google .. ok, the captive portal appears and asks for
a login. With the administration interface, I create a user, login, then
tries to redirect me to the site, good. Except that the connection is
never done ! After searching everywhere, I decide to use ssh to debug
the problem on the server. After a few strace commands, I found that
squid is trying to connect to the wrong host ! Yet another bug in the
installer …
After fixing a few more bugs, I finally succeed to use the captive portal.
Administration interface
The administration interface is nothing more than a user editor (it use
its own user database), and a few statistic tools like
AWStats and Firewall
Eyes. Ouch, a log analyzer !
This means you won’t be able to make complicated searches, and I have
serious doubts about the ability to parse big log files.
The captive portal software itself is
Chillispot, which is quite good but
appears to be unmaintained (no release since 2 years).
The log analysis tools are very poor, not to say rudimentary. There is
no easy way to find which user was connected on a host at a specific
date, you have to dig yourself through several poor interfaces,
connecting to the server and using grep is much more efficient !
Rules
Yet another surprise, there is no way to create rules to specify which
protocols are authorized. I was supposing that only HTTP and HTTPS were
allowed, but in fact when you are logged everything is open. No
tools are provided, so you have to know iptables well :)
Confidentiality
Alcasar generates a self-signed certificate and uses HTTPS connections
for login. This has to be treated seriously, because the certificate is
self-signed, so it will be quite easy to generate another self-signed
certificate with the same parameters to make a man-in-the-middle attack:
most people will only look at the certificate and then validate it
without questions ….
Strict security ?
Alcasar is developed by serious guys, and claims to comply with the
French laws. It also claims that it allows to authenticate users and
identify them strictly, and that these information could be used by the
police. Scary.
I decided to run a very simple test, to check if Alcasar would be
resistant to IP or MAC spoofing. I connected 2 laptops on the network,
and login on one of them. The following steps are very easy:On the
laptop not connected:
- start wireshark, and listen passively to get the IP and mac address
of the host In a few seconds, I got them
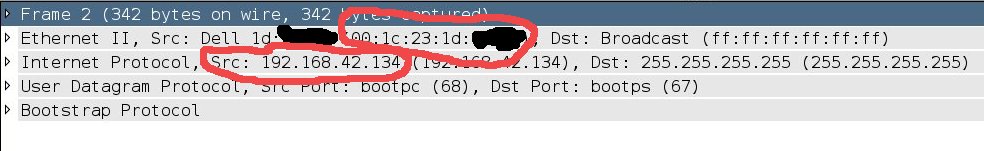
- change my IP and MAC addresses
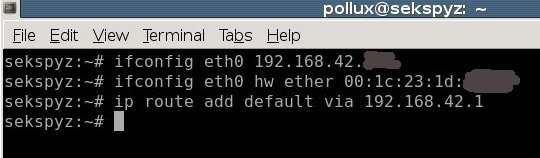
In fact, you do not have
to run the first and third commands: only change the MAC address and
launch the DHCP client. You’ll get the same IP address as the real host,
and the gateway will be configured.
Here you are ! In one command, you are connected !
Note: it is illegal to bypass a security protection. The commands here
are provided for educational purposes only, do not use them or you
could be prosecuted. However, the commands explained here are so easy a
child could use them, so you have to know them and to defend.
Am I caught ?
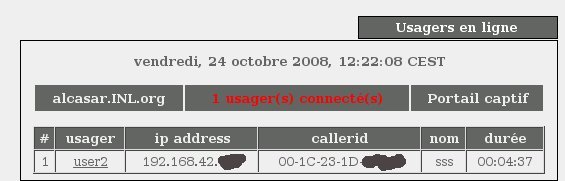
Alcasar haven’t seen the intrusion :) In fact, the problem is worse: I
am logged with the identify of the other user, meaning that my actions
will be logged with his name ! As there are no iptables rules by
default, I was able to connect to an SSH server outside without problems.
Conclusion
- Alcasar is only a set of scripts and configuration files based on other
- software. As for other captive portals, it is vulnerable to very simple
- attacks. The situation would not be as bad if Alcasar was not trying to
- present itself as a strict security solution. I would really be scared
- if my company was using a captive portal to handle internet access,
- because it gives a false feeling of security, can be bypassed very
- easily, and because of that, its logs cannot be used as legal stuff
- no serious judge would take into account a solution which can be
bypassed in a few seconds.
Captive portals like Alcasar provides a weak protection against attacks.
If you want strict authentication of users, and protection against IP or
ARP spoofing, use NuFW, it’s free (as free
beer) and free (GPL).
Update
Etant donné le nombre de questions qui me sont posées en privé par des
gens (venant du forum Ubuntu en particulier), je fais donc une mise à
jour (en français, vu le public concerné):
- Je n’ai rien contre les portails captifs, à partir du moment où on
les laisse dans cette catégorie (ouvrir quelques accès sans grand
besoin de contrôle ou de sécurité). Par contre, quand on prétend les
utiliser pour de la sécurité ou de la tracabilité, il faudrait
comprendre que ce n’est pas l’outil adapté
- Ethernet est un protocole qui n’est pas conçu pour de la sécurité.
Si la solution prétend solutionner le problème, tant mieux pour eux
(mais là comme ça j’en doute)
- Ce qui est aberrant c’est 1-le décalage entre le discours affiché et
la sécurité obtenue, et 2-la simplicité réelle du problème. Il
semblerait que d’autres s’en soient rendu compte sur leurs
forums, ou
comme sid (Cédric Blancher) l’a déjà montré pendant un
lightning.
Comme il le dit lui-même:
L'infrastructure mise en place, qui vise à authentifier les utilisateurs,
ne remplit pas son rôle. C'est mal, les administrateurs ont bossé pour
rien.
- Certaines personne n’ont pas compris le discours. Comme (toujours
par Cédric) explique dans cette
version
(excellente lecture, je vous conseille), il y a de très nombreuses
manières de contourner un portail captif comme alcasar, et
l’usurpation MAC/IP n’est que la plus simple d’entre elles. La
solution existe, et au lieu de bricoler sur des protocoles, il
parait plus sain de chercher une vraie solution (chercher du côté de
802.1x par exemple).
- Concernant le troll alcasar-nufw, je n’ai rien à dire, à part que
NuFW est dans Debian, donc que le côté libre n’est plus à démontrer
et que certaines personnes sur les forums en question racontent
vraiment n’importe quoi. D’ailleurs je ne vois en quoi les gens
comparent Alcasar et NuFW, le premier est un portail captif, le
deuxième un firewall par identité …